Do Carbohydrates Make You Dumber?
Carbohydrates are seen as something bad. However, they are essential to consume since they offer some benefits to the body. Oftentimes people fear gaining fat from eating carbohydrates. This should not be the only concern of eating large quantities of carbohydrates. It can also impact your intelligence to some degree. A perk to consuming carbs is that it reduces cortisol which is a hormone that keeps a person alert. Too much cortisol can make an individual feel stressed and moody.
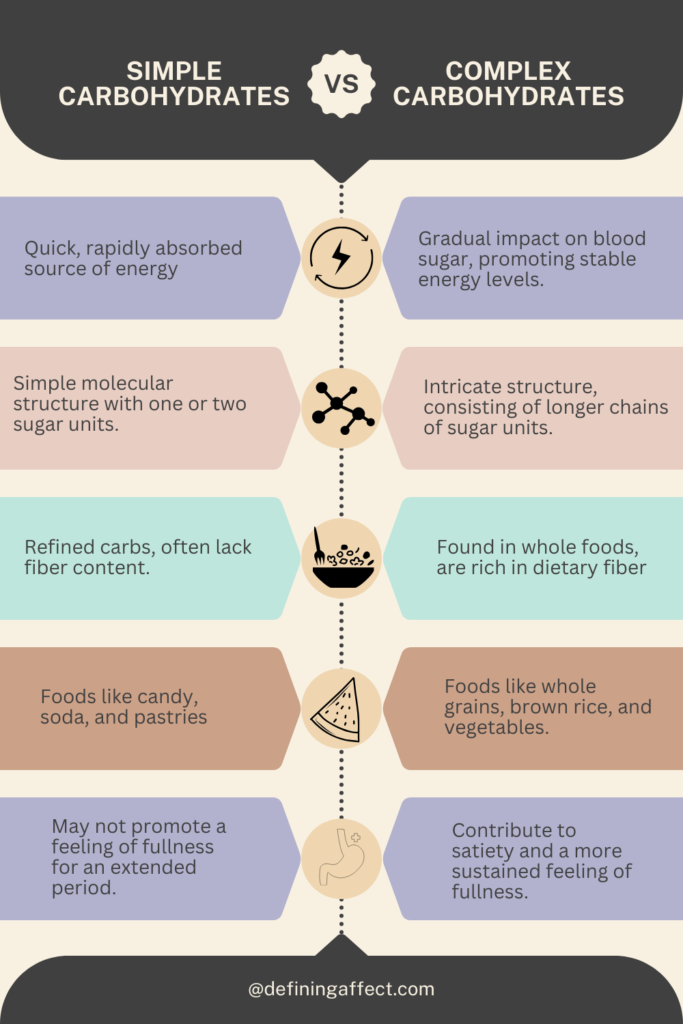
There are 2 different types of carbohydrates which are simple and complex. While they both offer some value to the body. They both are of a different quality. Simple carbohydrates are made up of sugars that are easily and rapidly digested, providing a fast burst of energy. It is as if a person takes a quick drink of espresso. Complex carbohydrates consist of long chains of sugar molecules. They are broken down more slowly, providing a sustained release of energy. Similar to slow-drip coffee, energy is being released gradually.
There are advantages and disadvantages to consuming either, but generally it is important to moderate daily consumption of carbs. For it does impact the body to some extent. When it comes to simple carbs it can make a person feel they have not eaten enough since they burn off quickly which can lead to an overconsumption of carbs (since there is a desire to eat more food). Hence eating more calories would result in weight gain (that is only if eating at a caloric surplus). However, complex carbs tend to keep someone satiated for some time and they take more time to digest. Although they both provide energy simple carbs tend to last the least amount of time therefore the feeling of “crashing” sets in. In other words, the individual is losing vitality. Since complex carbs take some time to digest it provides a slow release of long-lasting energy.
How Does Carbohydrates Impact The Brain?
Once the macro and micronutrients have been synthesized (from consumed calories). Carbohydrates influence neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine. Once serotonin is released it can make a person feel relaxed. When ingesting carbohydrates, especially those in sugary or starchy foods, the body starts a process that can produce a good feeling. The carbohydrates cause blood sugar to rise, and in response, the body releases insulin.
Insulin helps muscles take up most amino acids from the bloodstream, except for one called tryptophan. This special amino acid then becomes more available in the bloodstream. Tryptophan is like a building block that the brain uses to create serotonin, a feel-good chemical. So, when eating carbs, it’s like giving the brain the ingredients to make serotonin, which can set a positive feeling.
Serotonin does give peace of mind but it also converts into melatonin. Melatonin is a natural hormone that helps regulate sleep-wake cycle. This will make someone sleepy and truly relaxed. Moreover, this could be concerning since one can feel less energetic during the day. As mentioned previously vitality is impacted by this since the opposite of vitality is experiencing lethargy.
Does it Decrease Brain Power?
The overeating of carbohydrates can affect cognitive performance. A main concern of it all would be eating simple carbohydrates. As previously stated they tend to be easily digestible which could lead to feeling hungry most of the time. What could occur:
- Blood Sugar Fluctuations: Consuming large amounts of simple carbohydrates can lead to rapid spikes and subsequent crashes in blood sugar levels. These fluctuations can affect energy levels and concentration, potentially leading to periods of fatigue or “brain fog.”
- Insulin Resistance: Chronic overconsumption of carbohydrates, especially refined sugars, may contribute to insulin resistance. Insulin resistance is associated with impaired cognitive function and an increased risk of conditions like Type 2 diabetes, which can have cognitive implications.
- Inflammation: Some research suggests a link between a diet high in refined carbohydrates and increased inflammation. Chronic inflammation has been associated with cognitive decline and conditions like Alzheimer’s disease.
- Weight Gain: Excessive carbohydrate intake, especially when accompanied by a caloric surplus, can contribute to weight gain and obesity. Obesity has been linked to cognitive impairment and an increased risk of conditions affecting cognitive function.
- Neurotransmitter Imbalance: While carbohydrates play a role in serotonin synthesis, imbalances in neurotransmitters can occur with excessive or unbalanced dietary choices, potentially affecting mood and cognitive function.
Simple carbohydrates are refined most of the time. Usually, processed foods are quite addicting, so there is a tendency to eat more than a person shouldn’t. Behind it all is much of the sugar being in the body. Not only there are many health risks to excessively eating simple carbs. It also impacts the brain’s performance due to the fact of feeling fatigued. Generally, the person underperforms when experiencing lethargy. Because of this, there is a lack of drive and the feeling of engagement. Being aware or just making the effort to pay attention becomes difficult.
How Much Carbohydrates Should be Eaten Daily?
There is something called the keto diet and this encourages people to eat mostly fats and protein. This diet may not be the most sustainable as some may experience fatigue, irritability, and at some times hunger. In conjunction with this, it impacts hormonal output as it increases cortisol levels which is a stress hormone. The issue with stress it can cause some hormonal imbalances. Generally, the keto diet tends to force the body to make changes as this is something irregular. However, the keto diet is not entirely terrible, it is not worthwhile. It is good for a temporary time and to transition to another diet that would make maintaining oneself easier.
Returning to the question. It is more often dependent on the person’s size since everyone needs to eat a certain amount of calories and macros per day. There are a different set of ratios when dividing the amount of fats, carbohydrates, and protein that have to be consumed daily. According to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, individuals should be consuming at least 45% to 65% of their total daily calories. A ratio often recommended is 60% carbs, 20% protein, and 20% fats.
The ratio can be adjusted to the individual’s liking. However, sustainability is important to keep oneself healthy and energetic. The purpose is to moderate carbohydrate intake daily. There are variables that would need to be ruled out as well like sugar since carbs convert into sugars. So, there is no need to ingest foods that are loaded with glucose unless it is natural sugars.

Here is a sample for those who are mildly active.
NOTE: This is only a sample and the numbers shown may not apply to every individual.
Average Mildly Active Male (Example):
- Total Daily Calories (TDC): 2,500 kcal (for illustrative purposes)
- Protein: 30%×2,500 kcal=750 kcal (divided by 4 kcal/g)
- Protein: 188 g
- Carbohydrates: 45%×2,500 kcal=1,125 kcal (divided by 4 kcal/g)
- Carbohydrates: 281 g
- Fats: Remaining calories=2,500 kcal−(750 kcal+1,125 kcal)
- Fats: 625 kcal (divided by 9 kcal/g)
- Fats: 69 g
- Protein: 30%×2,500 kcal=750 kcal (divided by 4 kcal/g)
Average Mildly Active Female (Example):
- Total Daily Calories (TDC): 1,800 kcal (for illustrative purposes)
- Protein: 30%×1,800 kcal=540 kcal (divided by 4 kcal/g)
- Protein: 135 g
- Carbohydrates: 45%×1,800 kcal=810 kcal (divided by 4 kcal/g)
- Carbohydrates: 203 g
- Fats: Remaining calories=1,800 kcal−(540 kcal+810 kcal)
- Fats: 450 kcal (divided by 9 kcal/g)
- Fats: 50 g
- Protein: 30%×1,800 kcal=540 kcal (divided by 4 kcal/g)
If you want to learn more on how to increase metabolic rate check out this post!
Conclusion
In conclusion, a moderate consumption of carbohydrates is sufficient to keep one balanced. This coincides with hormonal balance. It is important to note complex carbs are superior to simple carbs as they provide a stable energy release and are least likely to cause inflammation. Simple carbs on the other hand can do some occasional good if needing a quick boost of energy but they have more negative effects on the body. More importantly, cognitive performance is something to be concerned about. Overconsumption of highly refined carbs can degrade brain power. Due to components such as serotonin and melatonin which makes the individual sleepy or fatigued. It is best to eat foods that are nutritional, wholesome, and minimally processed. For optimal energy levels, it would be ideal to eat 45% to 50% of carbs of the person’s daily caloric intake. Since carbohydrates convert into sugars it would be advantageous to limit consumables loaded with sugar.
If you found this post helpful, please share and subscribe!






